Blog
Reducing Supply Chain Cybersecurity Risks - 12 Tips for Manufacturing Companies
Aug 25, 2022
The manufacturing sector has seen increased pressure coming from worldwide cyber security attacks halting production and shutting down factories.
It’s important in today’s environment to ensure a high level of security to reduce the risk of disruption of operations as these can have massive monetary and brand impact.
In today’s issue, we’ll take a look at:
The 3 common types of cyber attacks in manufacturing.
Two case studies showcasing ransomware attacks in the industrial sector (i.e. hydraulic and defence)
12 Practical tips on how to best protect your manufacturing business.
More resources to up your organization's cyber security skills

Cyber attacks can halt whole production: image source
If you are a manager, an individual contributor to your supply chain or an executive worried about the possibility of a cyber attack, this post is for you!
3 Common Types of Cyber Attacks in Manufacturing
There are a few types of cyber security attacks that can cripple your supply chain that you should be aware of. Here are the 3 most common ones that you might have heard recently in the news targeting manufacturing companies.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that stops users from accessing files or systems by encrypting them.
The victim then pays the demanded ransom to the attacker, the attacker then provides the decryption key, which is then used to release/decrypt the files or systems.
These malware or malicious code are usually delivered through an email attachment, which when downloaded executes the malicious code and encrypts the files until the ransom is paid (which is not guaranteed).

Ryuk ransomware message
This type of attack is especially prominent in industries that need to constantly exchange information with partners. This is the case in manufacturing as usually more than 50% of the production is outsourced.
Phishing
Phishing emails are a social engineering technique for manipulating users so they give up confidential information.
Usually, these types of emails are based on principles like urgency (Eg, “The offer lasts only for an hour, hurry up and click the link) or authority (Eg, the Legal department asks for your date of birth, SIN…).
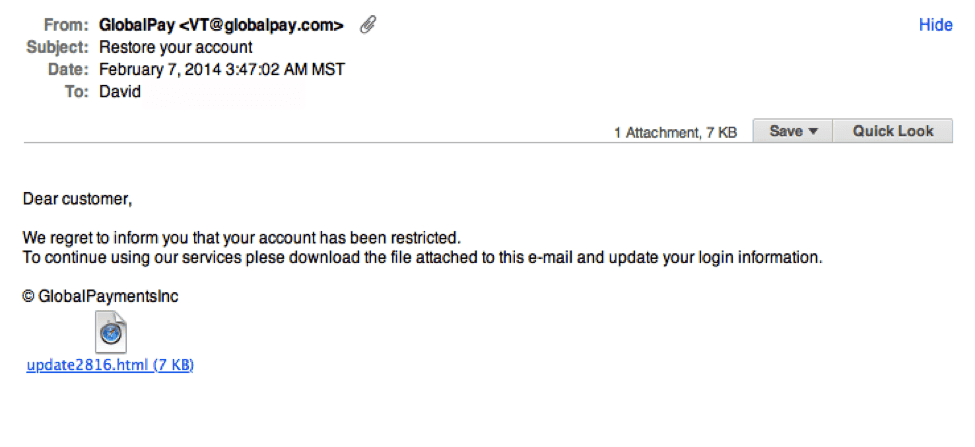
example phishing email
With most of the emails of your employee being available in lists that can be bought online this is a threat that can only be curved with proper employee discipline and security hygiene (more on this in later sections).
Credential stuffing
Credential stuffing is a kind of password brute force attack where the attacker attempts to obtain access to an account by using a list of commonly used usernames and passwords.
This log-in information list is generally collected from data breaches or stolen via phishing scams.

Diagram of a credential stuffing attack
Having a good enforceable security policy and password rotation schedule helps a lot for this kind of attack. More tips on how to set such a policy in a later section.
Let’s take a look at two case studies showcasing how Ransomware impacted two manufacturing companies in real life.
Case Study 1: 35 Worldwide Location of a Manufacturing Company Under Ransomware
Incident: At the end of January 2021, almost 35 worldwide locations of Palfinger were under a ransomware attack. Shortly after the attack came to light, the company shares, which had been listed on Vienna Stock since 1999, dropped by approximately 4%.
The company operations like email communication systems, ERP systems, etc. were stagnant for around ten days.
The company had to pay ransom to free itself from the attack, but the ransom amount paid wasn’t disclosed. The attack was not traced as it originated from the Darknet.
About the company: It is an Austrian company that manufactures hydraulic handling machines like loader cranes, tail lifts, marine cranes, etc.
Prevention tips:
Do not download attachments from unknown receivers or also one received from the known receivers, if you were not expecting any mail attachment from them. Always double-check with the known receiver over different mediums.
Take regular data backups to reduce the trouble faced during data loss.
Update your software as it may contain security patches of known vulnerabilities of the existing version of the software.
Disable macros from email attachments as when the user opens the attachment, it executes embedded code within it, which may result in infecting the system.
Before clicking on links, inspect them for typos and when you can traverse on your own to the required destination.
Avoid plugging unknown USB.
References on the attack:
Case Study 2: Electronic Components Provider for Defence Suffered from Ryuk Ransomware
Ryuk was largely spread through emails containing infected links or attachments. It was one of the most expensive ransomware as the ransom amount demanded was very high to free the systems from the attack when compared to other ransomware.
It had the capability of detecting and encrypting network drives and resources.
In addition to this, it also could delete data backup snapshots created on Windows endpoint systems, which makes data retrieval impossible if the Windows System Restore for users is disabled.
A certain version of this malware was also used to steal the file whose name/contents contained certain keywords like an agent, personal, hidden, court, etc.
This version of malware scans for file types related to C++ source code, Word/excel docs, PDFs, JPG image files, and cryptocurrency wallets.
Incident: In 2020, Electronic Warfare Associates (EWA) was also hit by the Ryuk ransomware. The data in the company’s web servers were encrypted.
Even after a week, when the company shut down its infected web servers, the traces were noted in the Google search cached results i.e., encrypted files and ransom notes.
About the company: It is an electronic equipment provider for customers like the U.S. Department of Defence, the Department of Homeland Security, etc.
Prevention tips:
Do not download attachments from unknown receivers or also one received from the known receivers, if you were not expecting any mail attachment from them. Always double-check with the known receiver over different mediums.
Take regular data backups to reduce the trouble faced in the event of data loss.
Update your software as it may contain security patches of known vulnerabilities of the existing version of the software.
Disable macros from email attachments as when the user opens the attachment, it executes embedded code within it, which may result in infecting the system.
Before clicking on links, inspect them for typos and when you can traverse on your own to the required destination.
References:
These are very scary examples that can impact any manufacturing business without a proper security habit in place. The more surface exposed to the attacker the higher the chances for this type of attack to hit the target.
In the next section, we will look at a few tips to upskill your manufacturing organization's security and prevent supply chain disruptions!
Security Tips
Tips #1: Passwords
Create strong passwords which are easy to remember. Create a password from your favourite phrase/song lyrics which is easy to remember, and make a meaningful pattern including letters and numbers on your keyboard for unique substitutions.
Make sure passwords are made up of a proper mix, at least 8 characters long, avoid using common words (eg admin) and substitution (eg‘@’ for ‘a’), rotate passwords at least every 6 months, don't reuse passwords, and use password managers.
Tips #2: Preventing vishing (voice + phishing) call
Don't respond to a question by pressing buttons
hang up call if you suspect it's fake and doesn't call on the call back number provided instead go to the official website to get the number
never provide sensitive info over the phone
next always personally double-check with the agency/department
also check the number to see if someone has already reported the number to be malicious.
Tips #3: Device Repair
backup your data
log out from your online accounts
lock your folders if not required
scrap deleted data
clear sensitive data like stored passwords, browser history, etc.
Tips #4: Backing up your data
Take your data backups regularly
create more than one copy of your data
have them stored in separate locations
use a standard naming convention so that it would be easy to identify files
decide which files need to be backed up, etc.
Tips #5: Sensitive information protection
Don't leave your devices unattended
Don't leave passwords written down in an accessible location
printouts containing sensitive info should be removed from the printers immediately
Avoid using public WiFi for critical transactions
Use VPN when logging into critical accounts
Access “HTTPS” authentic websites which means the channel is encrypted and has a valid certificate, etc
Tips #6: You clicked on the malicious link… now what?
take a deep breath first…
Then, disconnect the device from the Internet
Communicate with your security or IT department ASAP.
Scan the device
Use another device to change credentials
enable MFA
Backup data offline
Delete the email in which the link was received so you don’t open it by mistake.
Tips #7: QR code scanning
Use a QR code reading/scanning app that displays the complete URL of the website linked to the QR code
verify the URL of the site once the app has sent you there
verify that the company and the URL match
turn off any settings that take you to the scanned sites automatically
examine the QR code for evidence of manipulation; does it appear like someone has placed something over it? Etc
Tips #8: Safe web browsing
Don’t click on ads
use ad blockers (sorry google).
Avoid clicking on links that seem fishy
check for typos and don't trust shortened links.
Interact with well-known authentic sites.
Be cautious with online downloads.
Tips #9: About updating apps
Update your apps as soon as they are released as they contain security patches for known vulnerabilities of the existing versions. If not patched, there are chances of cybercriminals exploiting them to attain their malicious intent
Tips #10: Software Installation
While installing the software don’t just click next...finish. Carefully follow the installation steps as to what packages will be installed or what permissions are required/asked. Optionally, choose a custom installation to view details.
Tips #11: Phishing emails
Never trust email from the public domain authentic companies have their domain
check email structure (like spellings, and fonts)
always double check before downloading attachments if you were not expecting any
be creative with your answers to security questions as they form an additional security layer
use the answer that is difficult to guess and is not available over social media i.e., you can use a fake answer or use some random string
avoid clicking on the task link when you can traverse to the destination on your own as it is one of the common phishing email techniques “A task is assigned to you” as an attacker can easily mirror the email templates of these utilities.
Phishing emails have characteristics like urgency/emotional (Eg, “The offer lasts just for an hour, click the link), authority/trust (Eg, the Legal department asks for your DoB, SIN) or social proof (Eg, typo in company name).
Tips #12 Ransomware protection
Protect from ransomware:
avoid downloading email attachments if you weren't expecting any always double-check with the receiver over different mediums
take regular data backups
keep your apps up-to-date
inspect links before clicking
if possible traverse on your own to the required page
before clicking on links inspect them for typos or traverse on your own to the destination
disable macros from email attachments as when a user opens the attachment, it executes embedded code within it, etc.
Next Steps?
Security is a topic that should be on everyone's minds in the company. It’s the responsibility of all staff members to ensure that they are following best practices to not become themself a vector of social engineering attack.
Here are a few more resources that you can use to level up the security in your manufacturing business:
General Best Practices
These are for common attacks that cause breaches
If you are looking for a trusted supply chain partner with a security-first approach to software development, contact our team!
We have developed an e-procurement software that has been pretested with success multiple times with our manufacturing partners and that is trusted by the leader in aerospace, automotive and the mining industry.
We are also SOC 2 Type 1 certified and on track to hit our Type 2 by the end of the year! To learn more about why security is important for our head over here.
Have a great one and stay safe out there!
